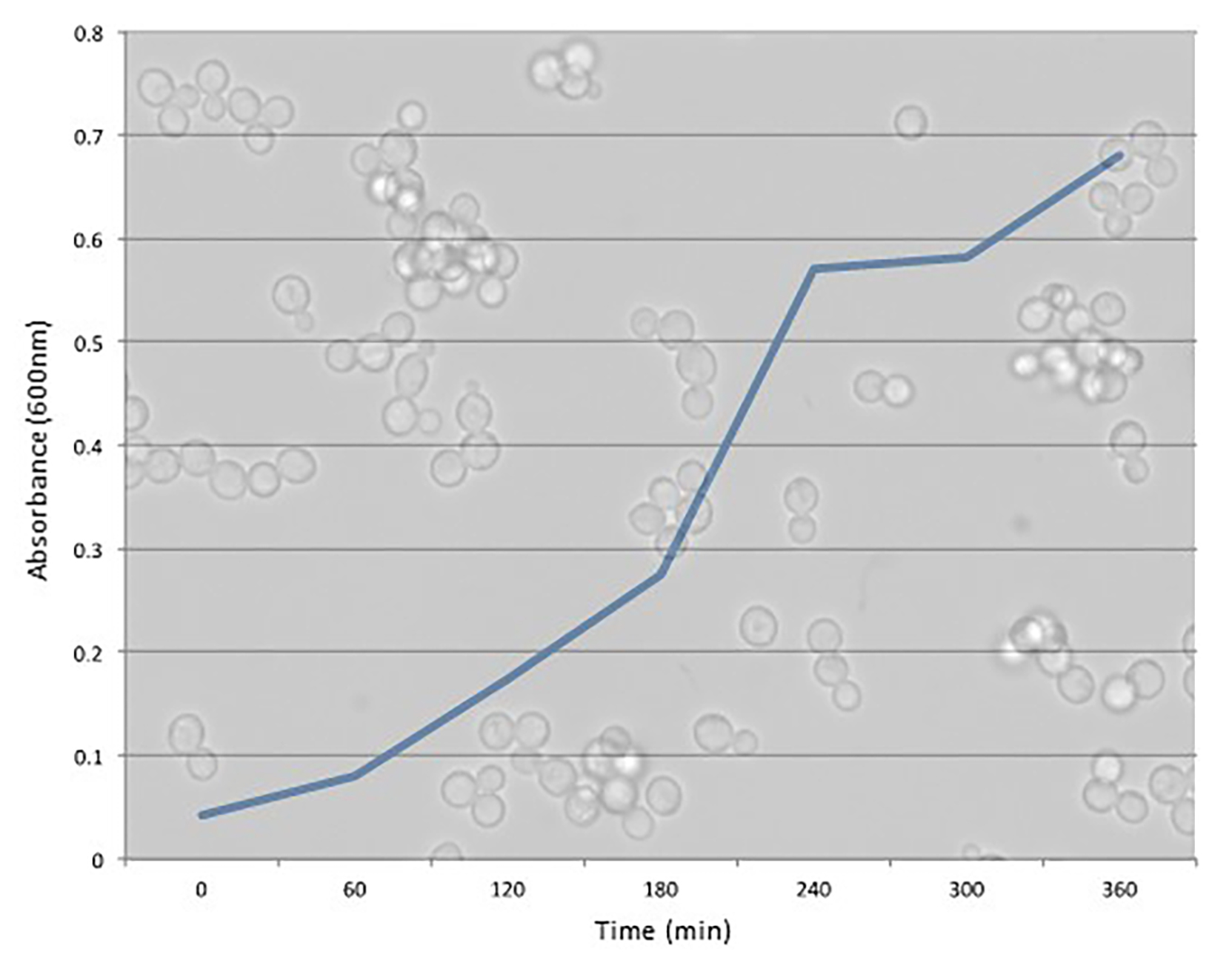
Traditionally-trained undergraduate students often lack an understanding of science as an active process that yields the information presented in their textbooks. One result has been a call for more research experiences built into traditional introductory undergraduate courses, now commonly referred to as course-based undergraduate research experiences (CUREs). The laboratory module presented in this paper used an established four-step pedagogical framework to simplify and streamline the development and implementation process of a CURE in an introductory biology laboratory setting. A unique six-week CURE was designed for undergraduates enrolled in a cell biology lab that employs Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a eukaryotic model organism. Students address a research problem that is of interest to the scientific community: Do select chemicals in the environment have adverse effects on the mitotic cell division? Students are first introduced to S. cerevisiae, its life cycle, morphology, growth curve generation and analysis, and the laboratory techniques required to cultivate this organism. Working in groups, students then act as scientists to research primary literature, ask an original question, develop a testable hypothesis, collaborate with peers, design and conduct an experiment, analyze and interpret data, and present their work to their peers. In addition, students are involved in multiple levels of iterative work, including addressing problems or inconsistencies, ruling out alternative explanations, and/or gathering additional data to support assertions.

Jeanne Sinara onto Cell Biology
@
on